Anti-reflux Mucosectomy for GERD
Gastroesophageal reflux disease, abbreviated as GERD, is a condition when your stomach acid comes back into the oesophagus from time to time. The oesophagus is the tube linking your mouth along with the stomach, and this backflow of acid (acid reflux) highly irritates your oesophagus’s lining.
Various people experience this acid reflux occasionally. However, if you experience constant acid reflux that arises more than two times a week, the chances are likely that you may be detected with GERD. In short, GERD is the long-standing, recurring incidence of Gastroesophageal reflux.
Treatment of GERD
Many people have shown to manage the distress of GERD with changes in their lifestyle and over-the-counter medicines. But for some, to manage the discomfort of GERD, there may be requirements of stronger drugs or even surgery to alleviate symptoms.
Your doctor may recommend first attempt alterations in your lifestyle and over-the-counter (OTC) drugs to manage GERD. If you don’t get relief even after some weeks, he may refer you to a gastroenterologist, a professional expert who specialises in gut treatment for further examination. A gastroenterologist may go for prescription drugs or surgical treatments.
Some of the OTC and Prescription medications options consist of the following:
- H-2 receptor blockers: These are medications to help reduce acid production for up to 12 hours. Stronger types are obtainable by prescription.
- Antacids: These offset the acid in your stomach with alkaline compounds and may offer instant relief. Side effects of taking antacids can comprise diarrhoea, constipation, or worse, kidney problems.
- Prokinetics: These medications help to empty your stomach faster. Side effects may include nausea, diarrhoea, and anxiety.
- Proton pump inhibitors: These are medications that prevent the production of acid and repair the oesophagus. These are a stronger version of acid blockers than H-2-receptor blockers and give room for impaired oesophageal tissue to get cured.
Some of the surgical options to treat GERD are as follows:
- Fundoplication: The surgeon binds the top of your stomach around the lower oesophageal sphincter muscle, tightening the muscle and averting reflux. Fundoplication is generally performed with a minimally invasive laparoscopic method.
- Endoscopic procedures: Various procedures use endoscopic sewing, wherein stitches are used to stiffen the sphincter, and radiofrequency that utilizes heat to generate minor burns to tighten your sphincter muscle.
- LINX device: The LINX device is a ring of small magnetic beads enveloped around the intersection of your oesophagus and stomach.
Anti-reflux Mucosectomy and Anti-reflux Mucosal Ablation for GERD
GERD is one of the most widespread gastrointestinal chronic diseases, and its incidence is increasing around the globe. Thanks to the upsurge in sedentary life and growing obesity counts, people are more disposed to develop GERD. The inclination towards processed foods high in salt, sugar, and saturated fats also poses a major factor in GERD.
Surgical interventions such as fundoplication are considered the most sought after treatment for proton pump inhibitor (PPI)-intractable cases but these cannot be looked upon indeï¬nitely as they pose long-term side effects while not providing optimal beneï¬ts in patients with volume reflux. Various minimally invasive endoscopic methods such as Anti-reflux Mucosectomy (ARMS) and Anti-reflux Mucosal Ablation (ARMA) for GERD have been established to manage this treatment gap.
Overview
Surgical interventions with methods such as Laparoscopic Nissen Fundoplication remains the most preferred standard of treatment. Minimally invasive anti-reflux intrusions are also available. ARMS is believed to be a safe and efficient endoscopic method of treatment that can be considered a choice preceding the surgical intervention. This technique has been refined, in which mucosal ablation is performed around the gastroesophageal intersection to trigger a restorative process to re-form the cardiac opening. The technique is termed anti-reflux mucosal ablation (ARMA).
What is the difference between Anti-reflux Mucosectomy (ARMS) and Anti-reflux Mucosal Ablation (ARMA)?
ARMA or ARMS are relatively new procedures developed to treat gastroesophageal reflux disease.
ARMA (anti-reflux Mucosal Ablation) comprises of ablation of the subcardial mucosa to stimulate scar retraction which, closes the cardiac incompetence. The main difference between ARMA with ARMS is that the gastric tissue is not removed but instead is destroyed to attain the identical effect.
How is it performed?
Gastric mucosal ablation can be performed both with Spray coagulation and using Argon-plasma, which is another customary procedure employed by many endoscopists.
Anti-reflux Mucosectomy (ARMS) is a fairly new-found endoscopic procedure meant for gastroesophageal reflux disease. A hemi-circumferential endoscopic mucosal resection (EMR) is done over the gastroesophageal junction (GEJ). This later contracts and strengthens during recovery.
ARMS seems to be a prudent method that does not impede forthcoming laparoscopic anti-reflux surgery when there is a failure. However, studies show that further tuning of the procedure and postoperative management might decrease the rates of dysphagia and the necessity for dilation.
Various studies and research also prove anti-reflux Mucosectomy to be safe and successful for the treatment of GERD. The studies also suggest that the outcomes are positive in the long run, and the response is stable and encouraging. But, suitable patient selection persists primal to the complete achievement of ARMS.
Conclusion
Many studies demonstrate that novel and innovative endoscopic anti-reflux procedures such as ARMS and ARMA show only decent short-range symptomatic progress but, long-term efficiency data are absent. Therefore, these less invasive techniques are not established or proven as standard treatment options, and studies are still undertaken to understand and determine the same.
Reference
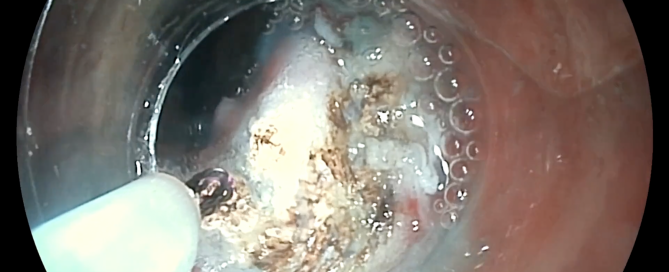
ARMA technique for the treatment of reflux
ARMA (antireflux Mucosal Ablation) consists of ablating the subcardial mucosa to induce scar retraction that … Continue reading
