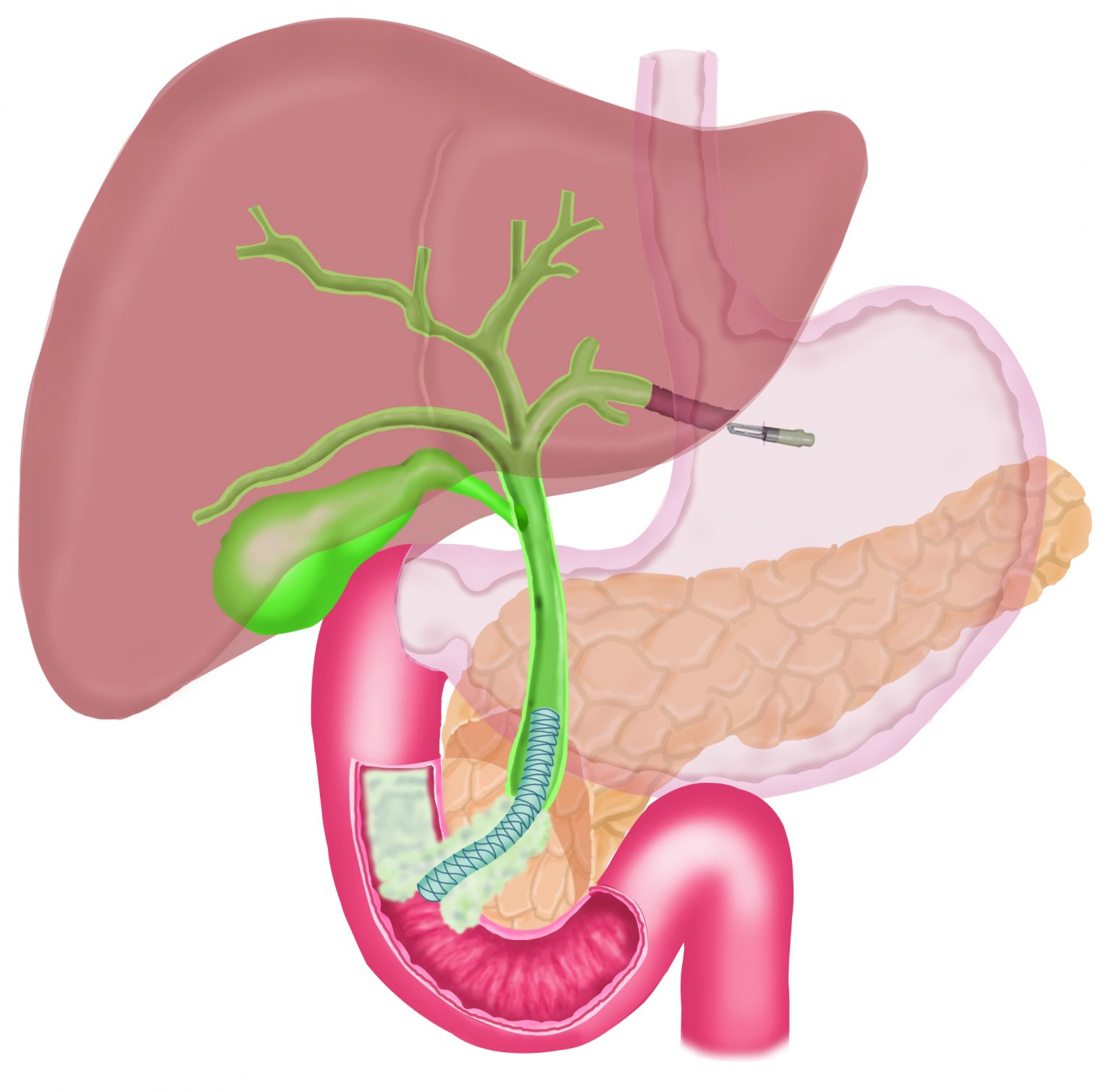
EUS Guided HepaticoGastrostomy
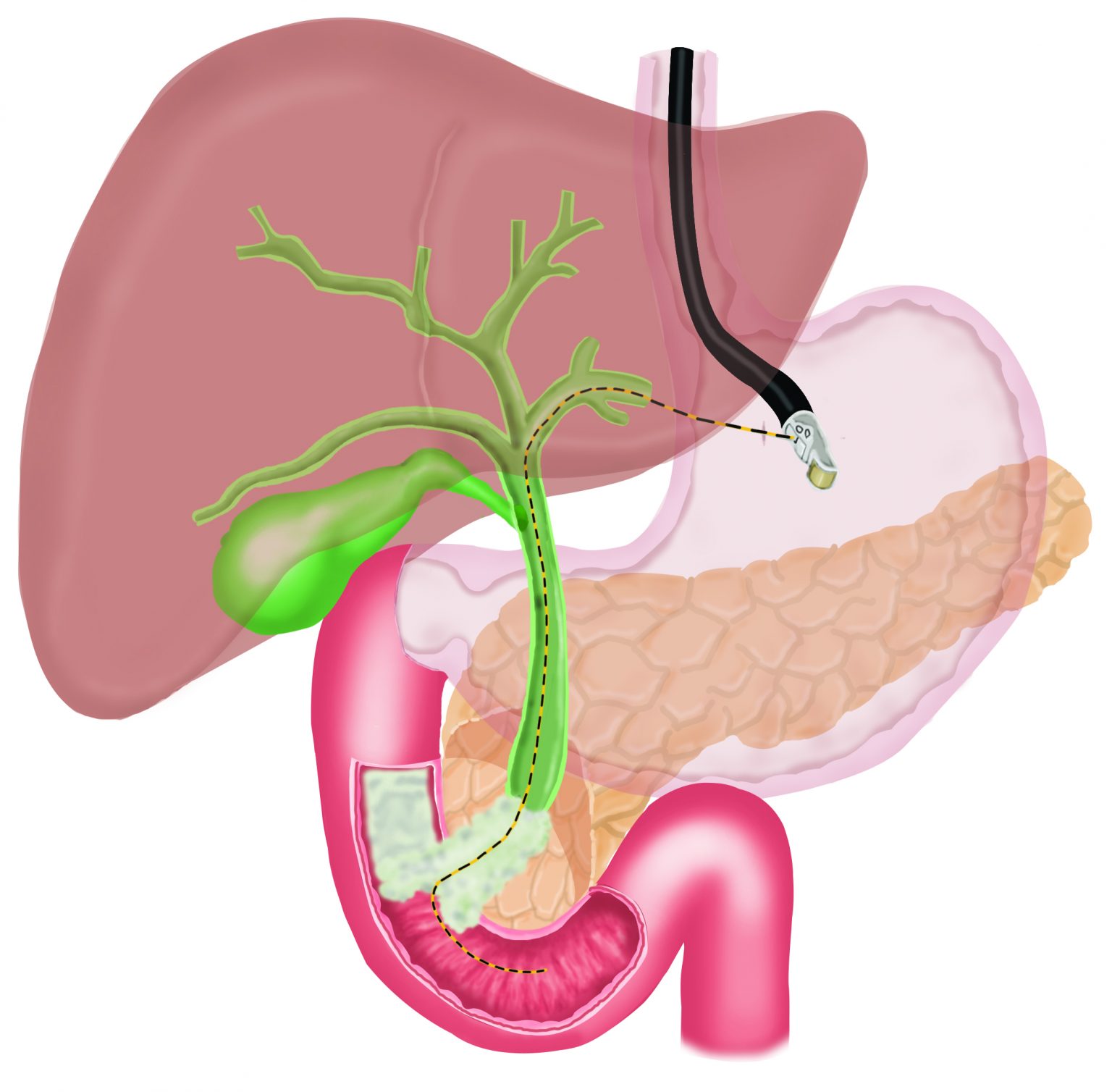
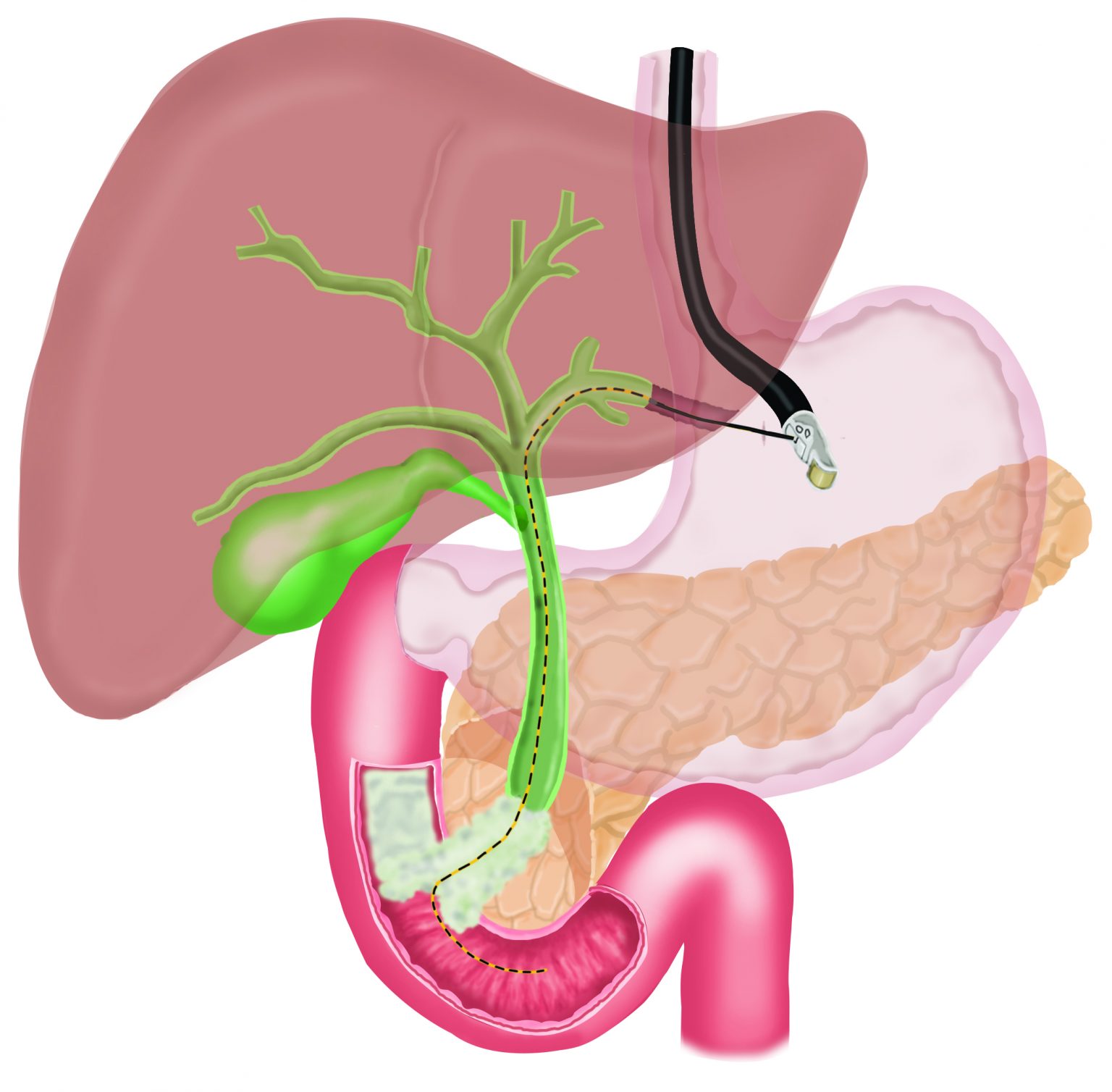
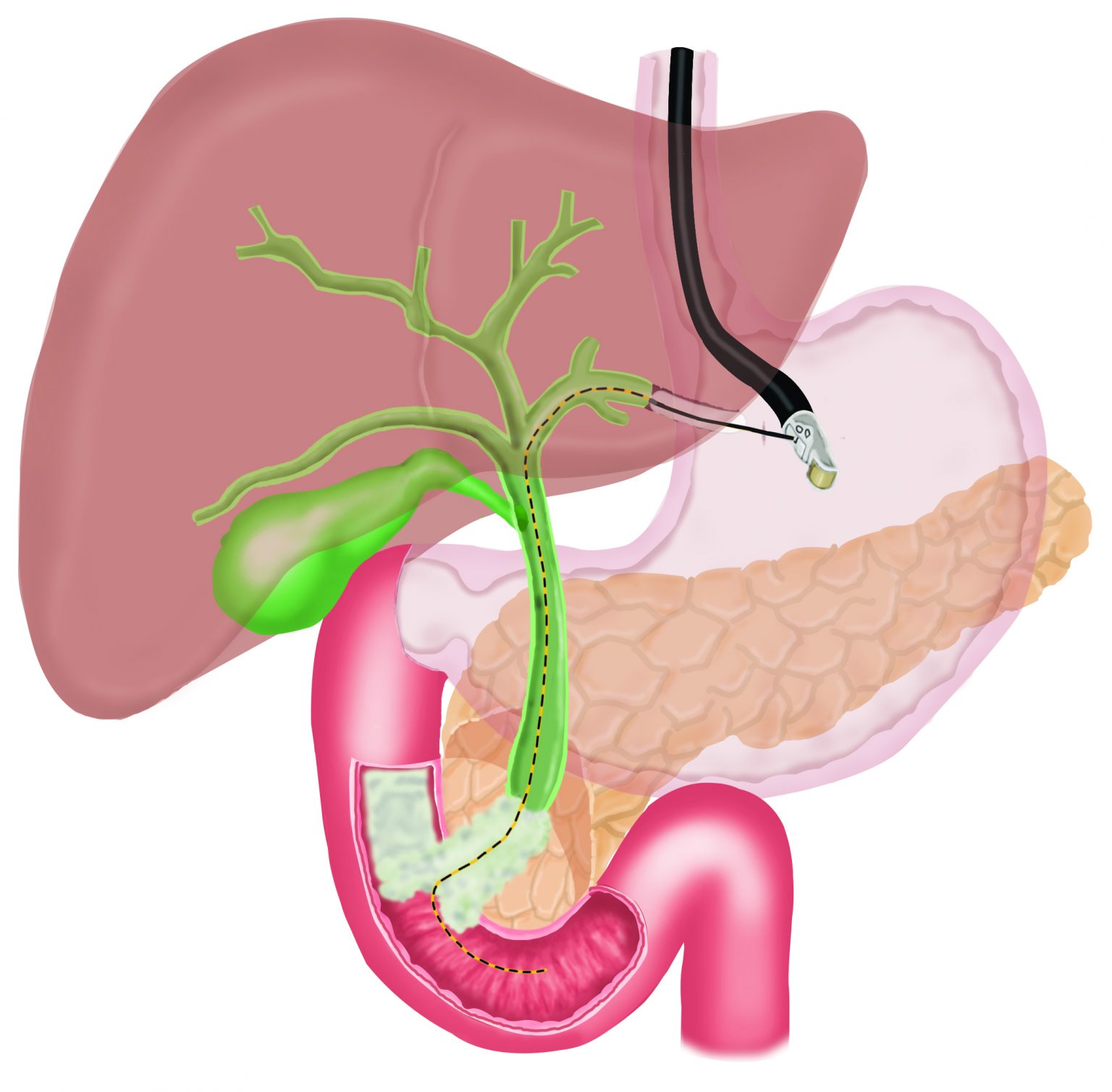
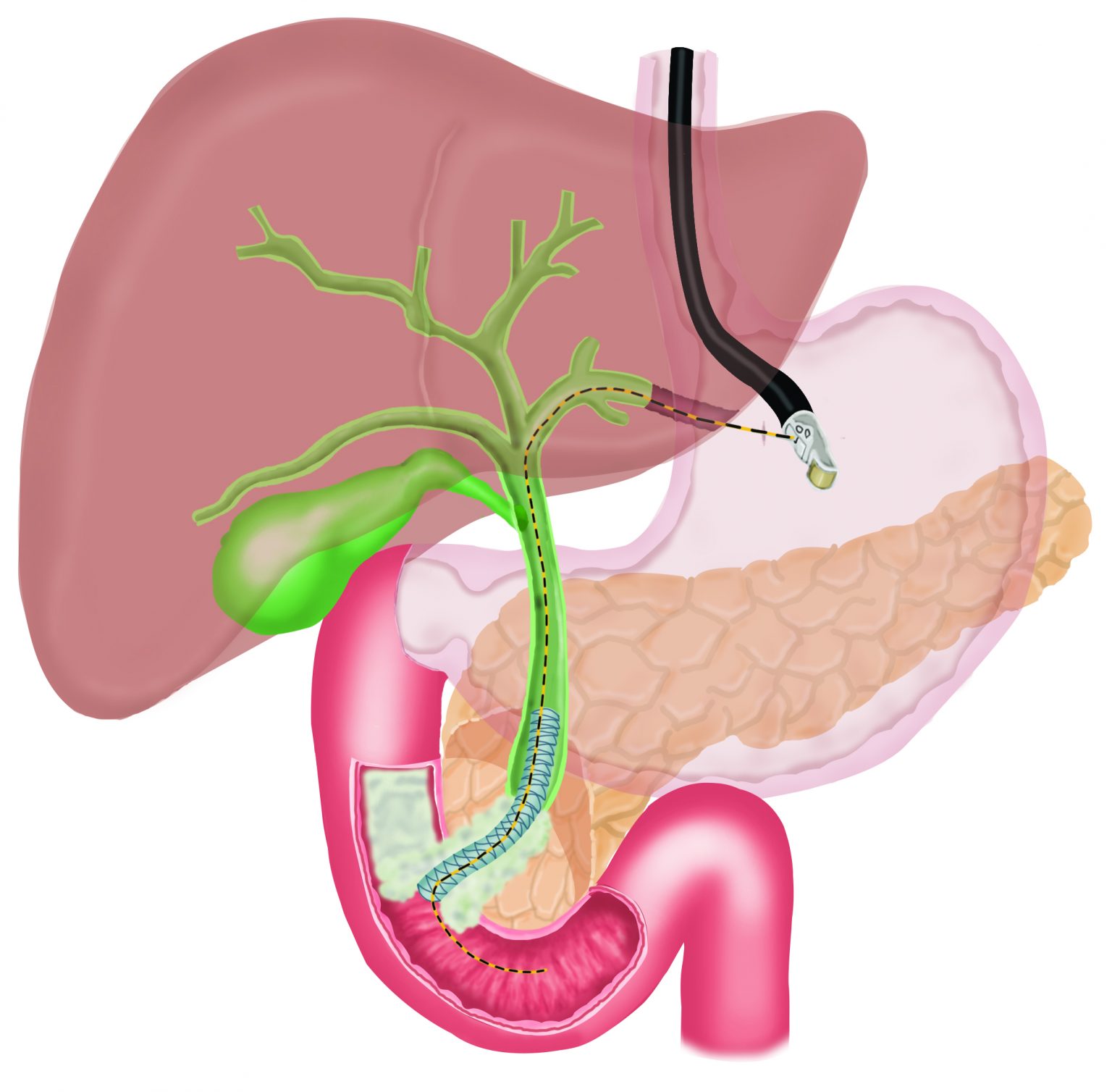
Jaundice can occasionally occur due to blockage of bile ducts, due to inability of the bile to flow into the small intestine and spillage of bile in the blood. Blockage of bile ducts can occur due to cancer involving the bile duct or the small intestine. Generally, a procedure called ERCP is performed to place a stent (metal or plastic tube) across the blocked bile duct to permit flow of bile into the small intestine and thus, relieve jaundice. However, occasionally ERCP is not possible due to inability to advance a wire or instruments in the bile duct. In such cases, a procedure called Endosonography (EUS) guided choledochoduodenostomy or Endosonography (EUS) guided Hepatico-gastrostomy can be performed.
In EUS guided hepatico-gastrostomy, under endoscopic sonography guidance, a wire is placed across the stomach wall into the bile ducts in the liver, followed by a “cystotome”, a device with cautery current to create a hole in the stomach and the liver, followed by placement of a metal stent across the stomach into the bile ducts in the liver to bypass the blockage. This allows free flow of bile out of the bile duct and jaundice improves. This is a painless procedure and performed under sedation.


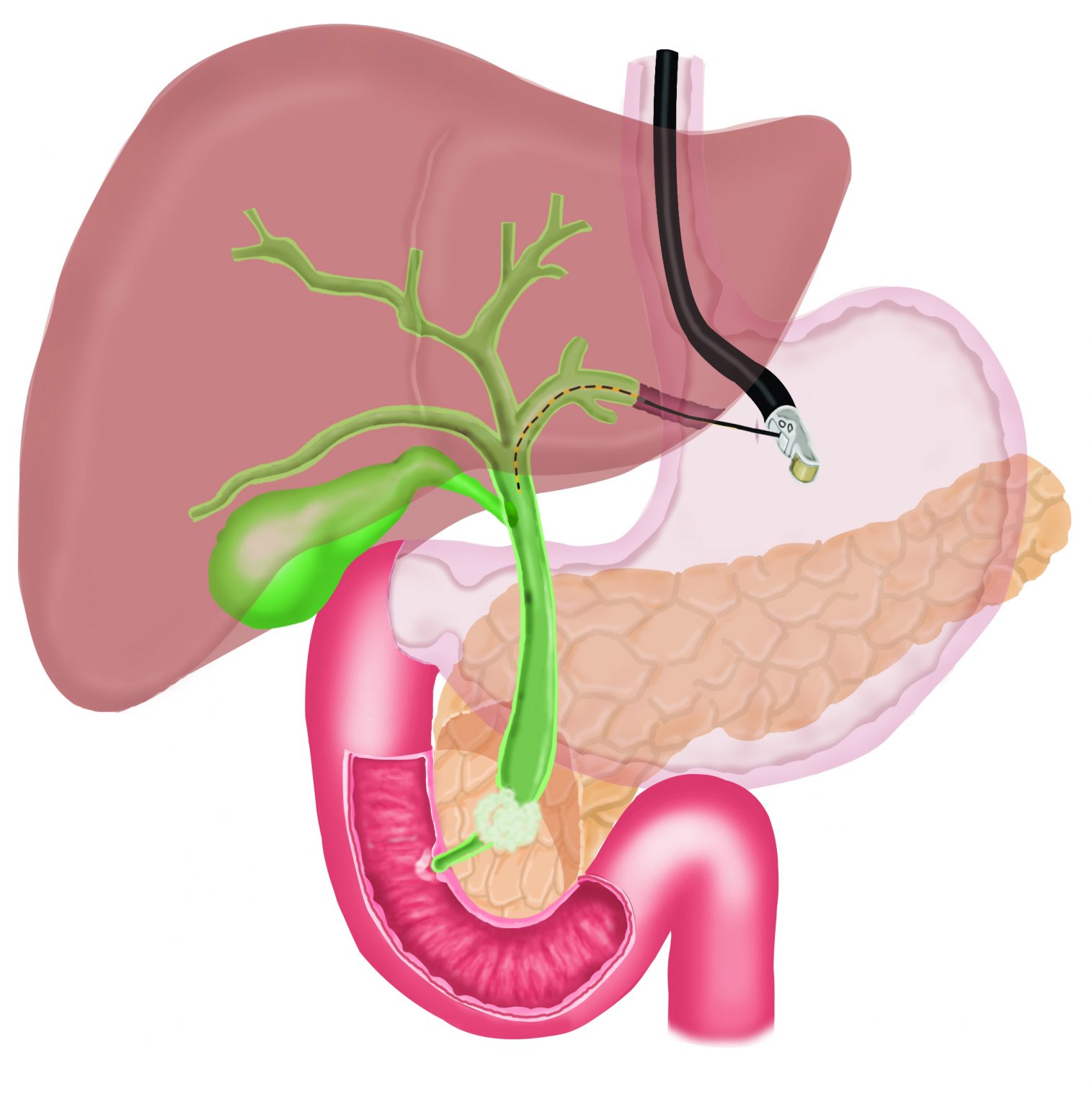
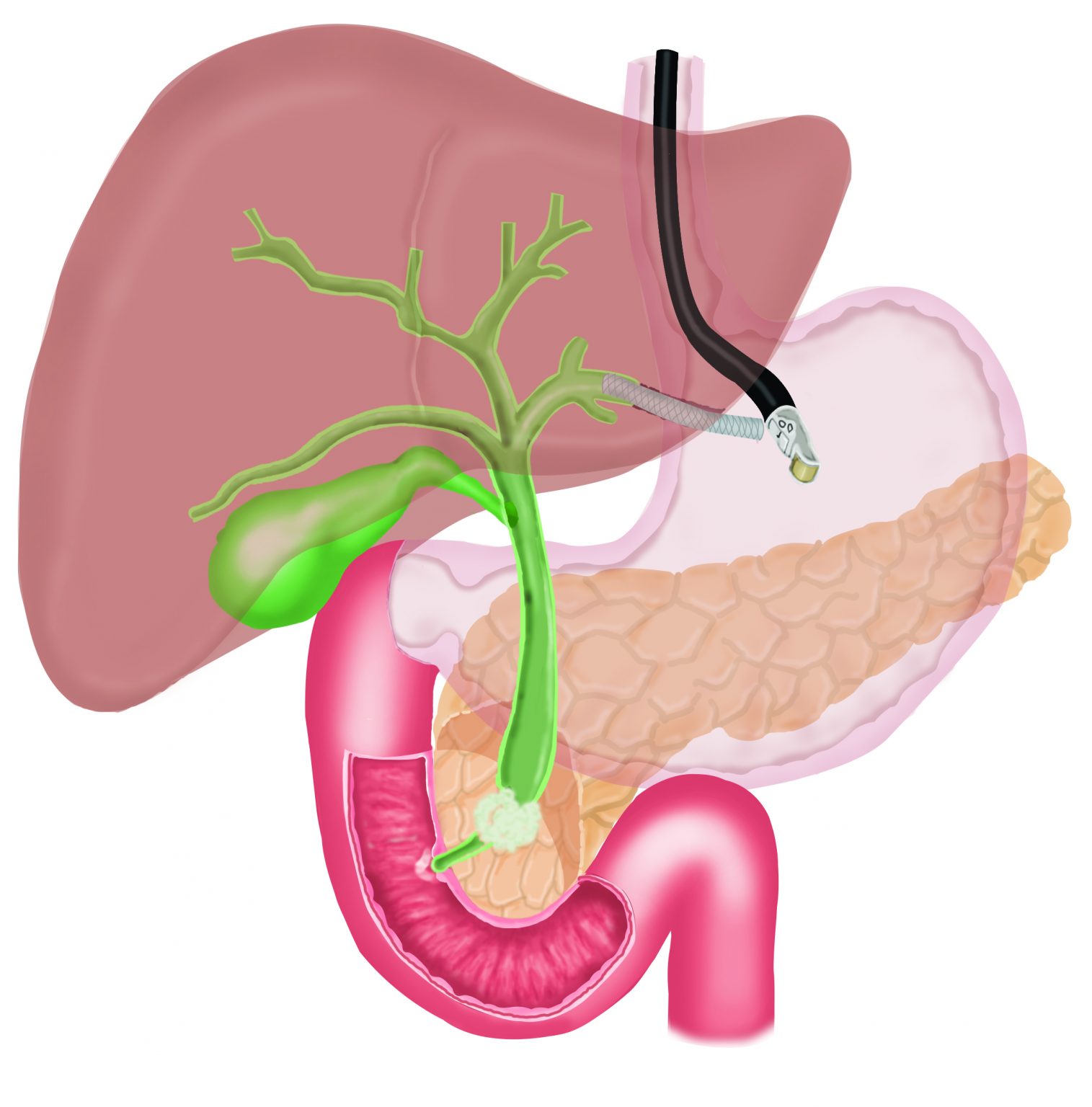

Transpapillary stenting via Hepaticogastrostomy