Bowel Disease Overview
What is a Colon Cancer ?
The large intestine or colon is where the salts and water content of solid water of digestion are reabsorbed before exiting the body. Most cancer patients fail to get an in-time diagnosis, and the primary tumour metastases and spreads.
The stages of colon cancer are:
Stage 0: This stage is called in situ carcinoma, where cancerous cells are present and are restricted to just the colon inner layers and hence treatable.
Stage I: Here, the primary tumour spreads from the inner layers but has not reached the lymph nodes.
Stage II: The cancer is deep-rooted and has already spread across lymph nodes, stomach lining and the inner layers.
Stage III: Cancer at this stage grows beyond the outer colon layers and reaches one of the three lymph nodes but has not spread to the stomach, spleen, liver etc.
Stage IV: In this phase, the cancer is widespread and reaches other organs like the liver, lungs, brain etc. It is hard to treat through drugs, while surgery/chemotherapy provides relief.
What are the causes of Colon cancer?
The most probable causes are:
- Most colon cancer cases form from adenomatous polyps, while it is rarely seen to form from benign Hyperplastic polyps.
- Genetic
- Attenuated familial adenomatous polyposis
- Juvenile polyposis syndrome
- Gardner syndrome a type of FAP
- Familial adenomatous polyposis (FAP)
- Turcot syndrome variant of FAP
- Lynch syndrome or hereditary nonpolyposis colorectal cancer
- MYH associated polyposis
- Muir–Torre syndrome variant of Lynch syndrome
- Peutz–Jeghers syndrome
- Age
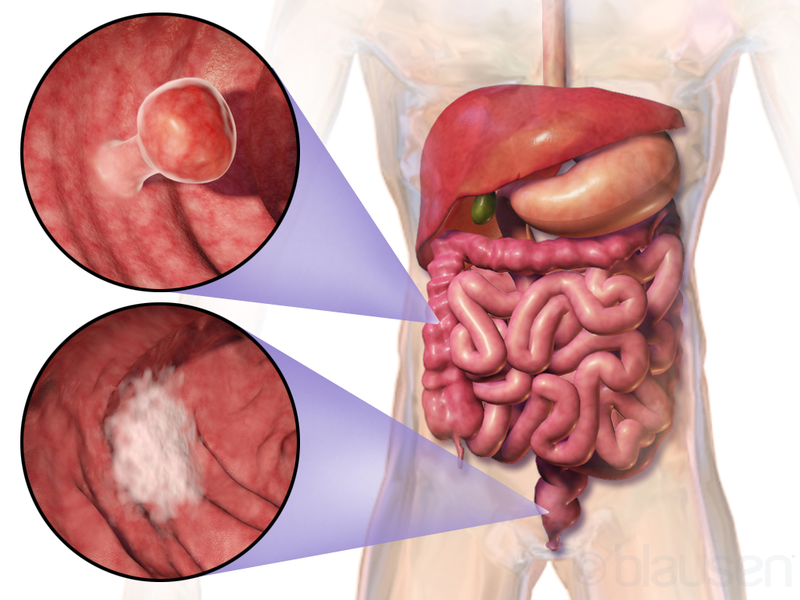

In India, 91% of those diagnosed with colorectal cancer are in the 50 age group. Obesity, poor nutrition, inactive lifestyles, low-fibre diets and those using tobacco are at higher risk.
Underlying conditions like those below also are probable causes:
- Having undergone radiation therapy for other "cancers"
- Diabetes
- Crohn’s disease, IBD or inflammatory bowel diseases or ulcerative
- pylori infections causing ulcers that can lead to colon cancers.
- Gastritis inflammations can cause pernicious anaemia leading to cysts and polyps that may lead to cancer.
- Growth hormone disorder or
In children:
Infants rarely manifest colon cancer. Children don’t fare too well with colon cancers, and as such, colon cancer takes time to form and is a disease of the adults and elderly.
In pregnant women:
Pregnant women with colon cancer symptoms of vomiting, rectal bleeding, nausea etc., may treat these as pregnancy symptoms. This delays timely diagnosis, malignancy and has a high metastatic spread.
What are the symptoms of Colon cancer ?
Symptoms may include:
- Feeling bloated after eating
- Feeling full after eating small amounts of food
- Heartburn
- Indigestion
- Nausea
- Unintentional weight loss
- Vomiting
- Constipation
- Diarrhoea
- Changes in bowel movements or blood in stools
- Loose stools
- Abdominal cramps, pain, gas or bloating
- Repetitive urge to defecate
- Fatigue/weakness
- IBS symptoms
- Iron deficiency/anaemia
Other symptoms noticed are
- Fever
- Vomiting and blood in the stools
- Cramps
- Enlarged spleen and abdomen
Note: Midas Hospitals recommends that cancer needs urgent diagnosis and treatment as recommended by a team of oncologists, gastroenterology and physicians.
How is colon cancer diagnosed?
Colon cancer, when suspected by the doctors, is usually symptomatic-based and includes a:
Physical exam: The doctor generally will check symptoms like stomach pain, bloating etc., alcohol consumption, medical history and medications taken. The doctor may check for pain, swelling and tenderness by applying hand pressure on the belly region.
Blood, DNA and stool tests to assess cancer. Imaging tests:
- Ultrasound scans of the stomach
- CT and PET scans of the abdomen
- MRI scanning
- Barium meal test with stomach x-rays. New tests like Cologaurd or capsule coloscopy
- Colonoscopy and Sigmoidoscopy where a camera in a small pipe is non-invasively used to study the colon tract and conduct needle-aspirated biopsies
Organ function tests:
- Liver (LFT) and Kidney function tests
- EKG or echocardiogram
Invasive tests like biopsies:
Laparoscopic surgery/ biopsy where a small tissue sample is used to detect cancer. If it is cancer, then further tests are ordered like the
HER2 testing
This cancer is caused by an excess of the HER2 growth hormone and can be treated with drugs targeting this protein.
Protein and gene testing:
These tests are for PD-LI immune checkpoint protein, dMMR, a mismatch repair gene and MSI-H or microsatellite instability, TMB-H high tumour mutational burden are treated with Keytruda (pembrolizumab).
Targeted testing:
Testing is done for NTRK gene testing may use drugs to target the gene.
What is the treatment for Colon cancer ?
Treatment options are dependent on the cancer type and treated by teams of doctors. Some options are
- Surgery
- Chemotherapy
- Radiation therapy
- Clinical testing trials and targeted therapy
Note
- Cancer treatment depends on the stage of cancer
- Cancer treatment has many physiological, mental, financial and societal side effects
- Follow-up tests and biopsies of lymph nodes and other affected body parts may also be needed
What a patient of Colon Cancer can do to lower the risk of colon cancer?
There are things you can do that could lower your risk of stomach cancer.
- Maintain a healthy weight
- Eat a balanced diet
- Get some physical form of exercise
- Drink green tea
- Eat high-fibre vegetables and fresh fruits while avoiding aspirin, alcohol, smoking, sugary beverages, red meats and processed foods
- If over 50 years, get screened for cancer and predisposal factors
What are the warning signs ?
If you observe any of these symptoms, Medical Hospitals suggests you consult a doctor urgently.
- Blood in the vomit or stools
- Coronary problems
- Bloody stools or brownish urine
- Severe constipation, no urination and impaired bowel movements
- Confusion, tiredness and daytime sleeping
Note: These conditions are serious, and Midas Hospitals recommends screening and an Oncologist consultation.
Remember:
If you have any or all of these symptoms mentioned, approach the doctors in Midas Hospitals for cancer evaluation and treatment. Stick to the cessation of smoking and liquor to prevent further inflammation and never self-medicate.
What is the outlook for colon cancer patients?
60% of colon cancer patients beat the 5-year survival rate.
What is the estimated cost of colon cancer treatment in India?
The colon cancer treatment cost in India depends on the location, cancer stage and hospital and could range from 2.75 to 4.5 lakh.
Why is colon cancer rare in kids?
Most times, colon cancer is from polyps, and these take an average of 10 years to turn cancerous. Hence it is rare in infants and young children if you consider all below 18 years as children.
Can colon cancer reoccur?
If all the cancerous cells are killed, there would be no reoccurrence. However, after a year, the cancer cells could show up in distant organs.
Are blackish stools a cancer sign?
Yes. Tarry or blackish stools are signs of cancer, especially when accompanied by pain, feeling bloated, gas etc.
How long does one live with colon cancer Stage-4?
No one can predict death. But, 14% of stage -4 patients with colon cancer live past the 5- year survival mark.
Reference
Reference:
https://docs.google.com/spreadsheets/d/1kblLjTTnmPbcJFuZQ0piYRbs3sBKCxWw/edit#gid=1586350786
https://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/colon-cancer/symptoms-causes/syc-20353669
https://www.webmd.com/colorectal-cancer/guide/understanding-colorectal-cancerdetection-and-treatment
https://www.medicalnewstoday.com/articles/150496#outlook
